
- New study suggests EVs cost more to insure than gas cars, but comparisons seem mismatched.
- Critics highlight flawed methodology and unclear data controls that may skew the findings.
- While EV repair costs are high, warranties and modern engine replacements blur the gap.
Love’ em or hate’ em, electric vehicles are, on average, pricier to buy than their ICE counterparts. A new study suggests that they’re more expensive to insure as well – and we’re not talking about a few basis points. However, after digging into the details, the results are not as clear-cut as they seem.
More: Filing A $100K Insurance Claim For A Crash Works Better If You’re Actually In Your Porsche
The data in question comes from a study by Insurify. It leveraged over 97 million insurance quotes to determine the average rate for gas-powered and electric cars. Rates reflect full coverage on a 2020 model year or newer. In most cases, the quoted figures reflect a driver with a clean record and good or better credit. Overall, it says that EV owners pay 49 percent more to insure their cars.
Why Rates Run Higher
The explanation seems straightforward enough. EVs come with higher costs to start with, even when compared directly with gas-powered competitors and they’re typically more expensive to repair when they’re damaged. Parts are harder to come by and a damaged battery, for instance, can write off a car faster than an average engine failure.
On top of all this, keep in mind that EVs are often very new models with little to no aftermarket or junkyard support. It’s no wonder that insurance companies might build in a buffer for that risk.
Question Marks in the Data
Despite that, there are some questionable bits with the study. Some of the matchups mentioned raise eyebrows. For example, it directly compares the Tesla Model X to the Audi Q3 and the Mercedes A-Class goes up against the Tesla Model 3. These, however, aren’t really apples-to-apples comparisons, as some on Reddit pointed out. As one commenter put it, “Some of these comparisons make genuinely zero sense.”
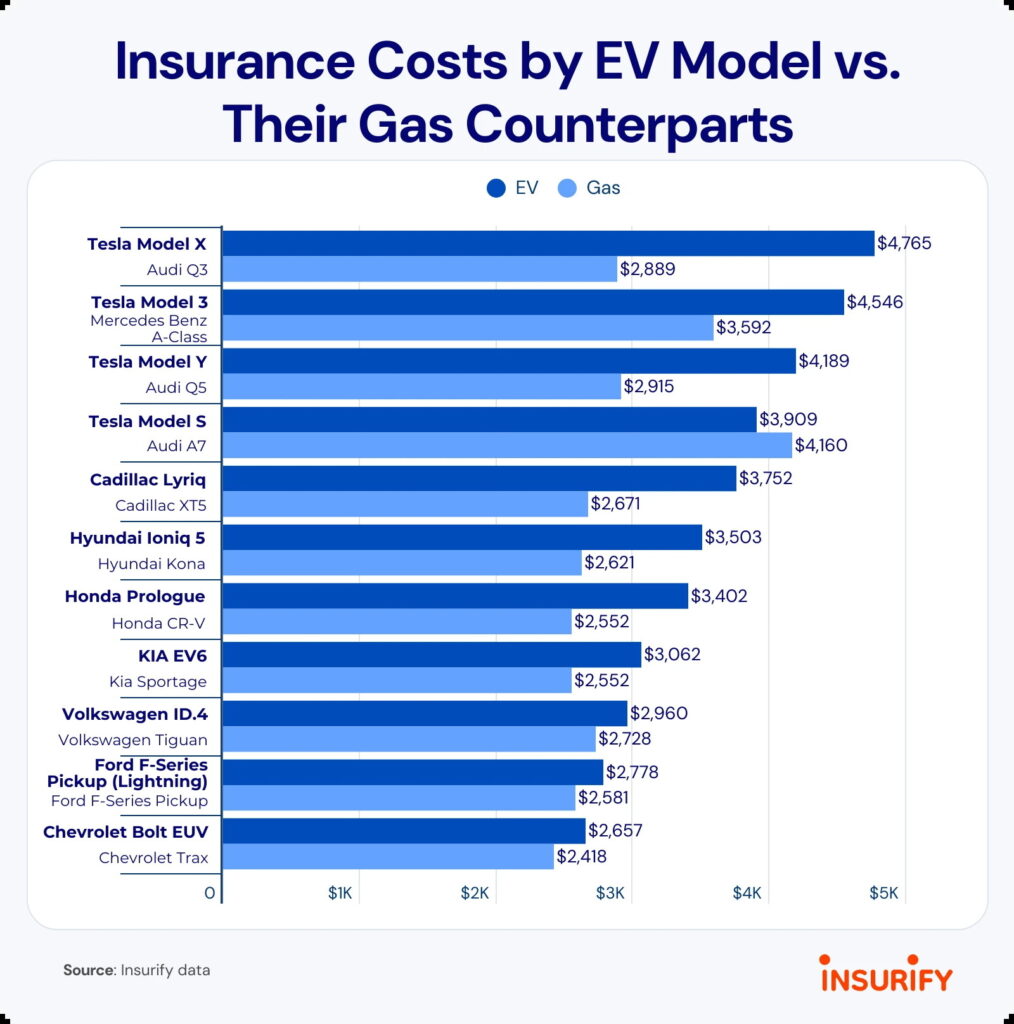
What is important to note is the fact that ignoring certain factors like real-world repairability, warranty coverage, or depreciation curves, could tilt the figures against EVs quickly. In addition, each repair case is, to one degree or another, unique.
For example, while engine replacement typically isn’t as costly as a battery replacement, the true cost depends entirely on the car in question. On top of that, the federally mandated 8-year/100,000-mile EV battery warranty offered on every new EV reduces risk for owners, a factor that insurers might not fully weigh.
A Few Useful Takeaways
Even with the caveats, the study did highlight which EVs are cheapest to insure. Models like the Chevrolet Blazer, Nissan Leaf, Kia Niro EV, Hyundai Ioniq lineup, Ford F-150 Lightning, and the Subaru Solterra/Toyota bZ4X twins all made the list.
Still, whether the numbers are genuinely meaningful is up for debate. Insurance for EVs might trend higher for the time being, but with questionable methodology and comparisons, this study might say more about how we measure costs than it does about EV ownership.
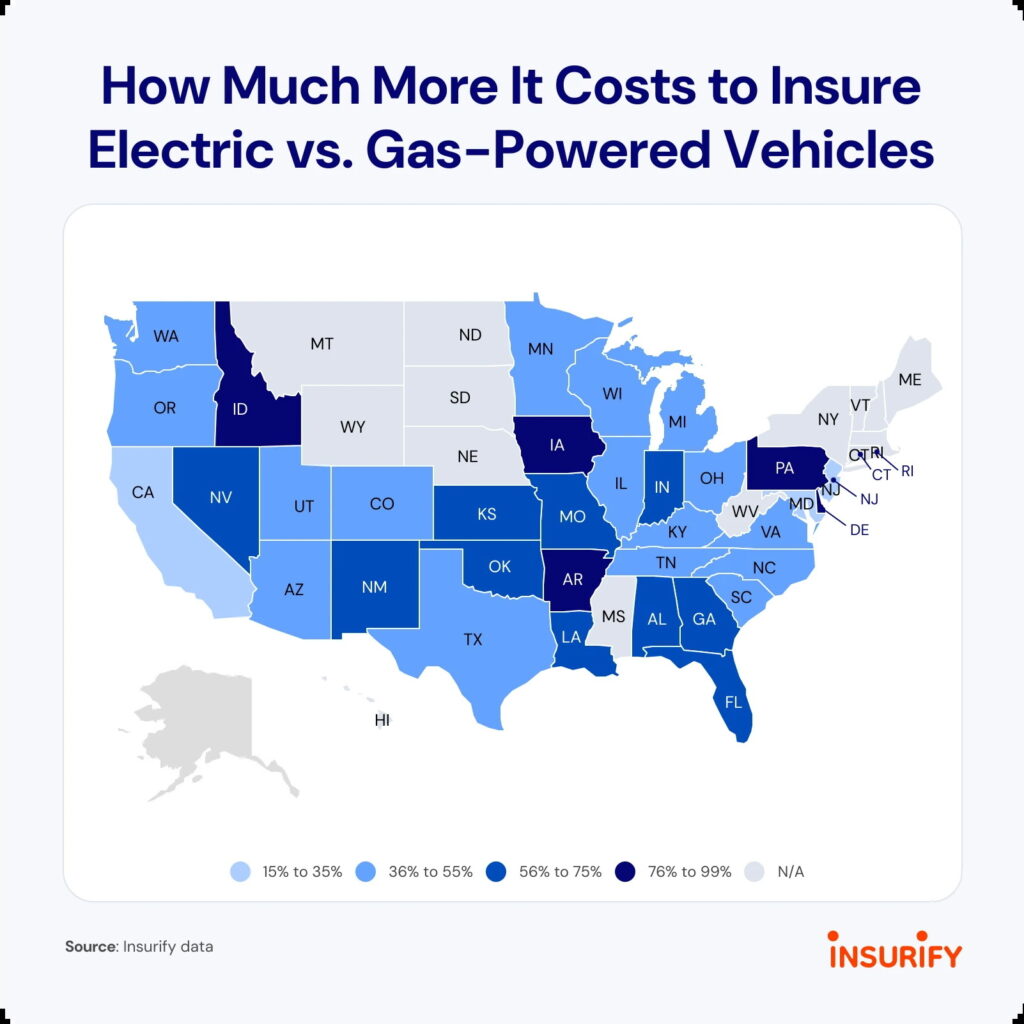
Credit: Insurify


